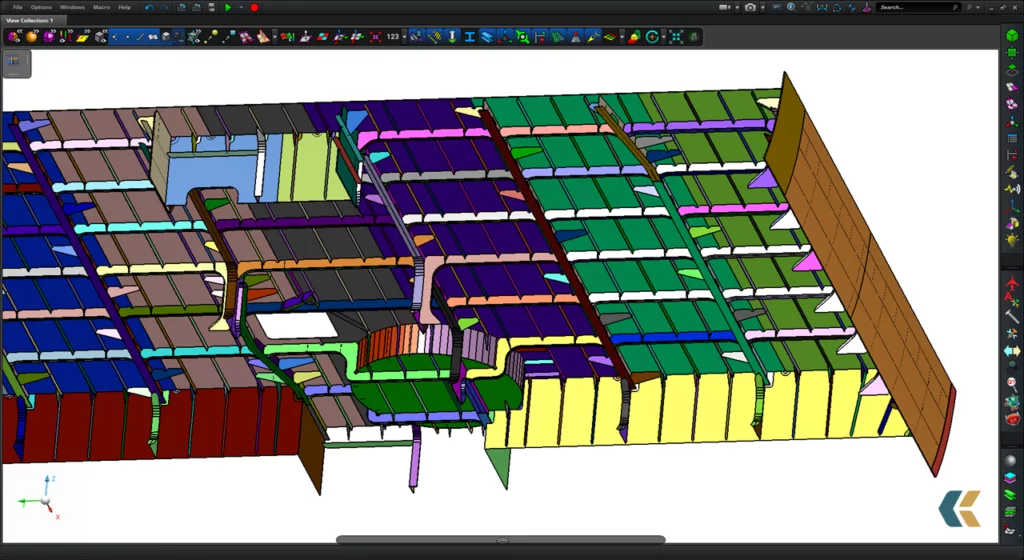
FEM analysis: the correct preparation of the calculation model
The calculations model’s preparation is the embryonic phase of the FEM analysis and has a crucial role for its proper development. In Kyma has been developed a procedural process that allows to optimize time and resources by cancelling the analysis errors related to this phase.
“Garbage in, garbage out”
One of the most significant axioms that the FEM analyst must keep in mind is “garbage in, garbage out” which technically means: if the operator introduces “garbage” in the calculation model, the solver will return “garbage/junk” in the form of incorrect results.
This is a mantra concept in Kyma because it clearly expresses a pivotal principle: every stage in the FEM’s model preparation is crucial.
Three macro-categories for step-by-step analysis
Precisely because each phase of the calculation model is fundamental, its stages of preparation, in Kyma, have been divided into three macro-categories that allow to proceed step by step to the control and verification of its quality.
1) Geometry creation and import
The three-dimensional geometries allow to analyze very extensive and complex structural systems typical of recreational vessels’ design.
The CAD software dedicated to the marine industry has work-tools much more efficient and faster than the CAD modules internal to pre-processing graphical interfaces, generally primitive and cumbersome. Depending on the type of verification to be carried out in fact, the designer will be able to correctly design the structure to be analyzed and, eventually, start the first phase of defeaturing, removing, for example, construction details or structural elements not critical for the validation of the calculation and the correctness of the structure.
The obtained 3D model can be exported in multiple exchange formats such as iges, step and parasolid necessary for the subsequent import in the working environment of FEM software.
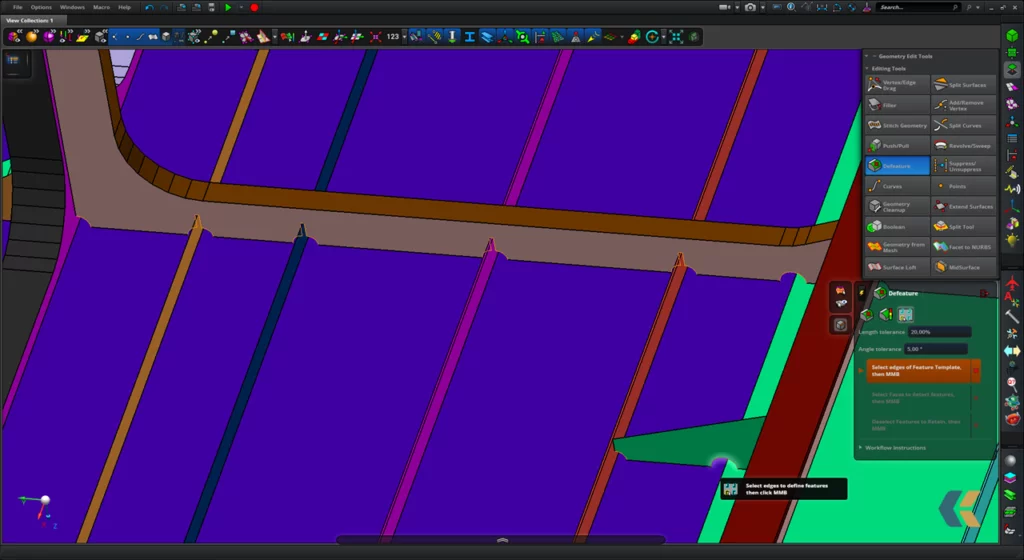
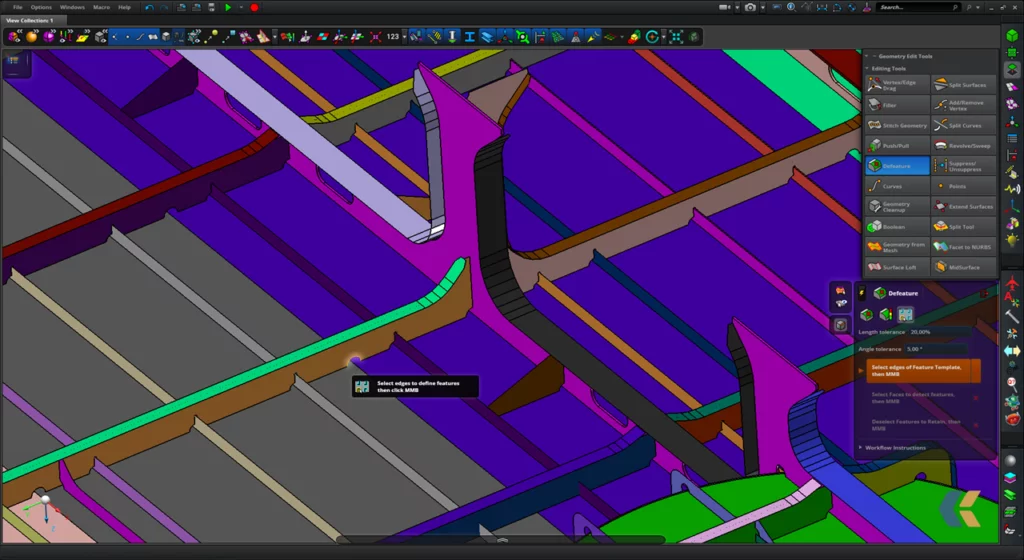
2) Defeaturing
The Defeaturing is the crucial phase of the calculation model’s preparation, in which the FEM analyst decides what is superfluous and what is indispensable for a correct verification and validation of the FEM model.
For example, a very extensive calculation model that aims to minimise the distribution of structural displacements subjected tospecific design loads, can be performed by omitting small notches or holes, crossings between secondary and primary structures (cut-out) etc.
Conversely, a detailed analysis focused on a small portion of the structure that aims to assess the maximum stress at a critical point (peak stress) it must contain all possible information relating to the geometry analysed in order not to have any kind of simplification potentially risky to generate incorrect or misleading results.
A further example would be where imported CAD geometries contain the solid representation of various structural elements, including theirthickness. Thanks to the advanced tools available in MSC Apex©, the FEM analyst in a few steps can obtain the information necessary for their correct physical and numerical representation, extracting the midsurface, thus representing as realistically as possible the main geometric properties of the structures (area, inertia, section modul etc.) and always obtain realistic results.
3) Breakdown of the structure
The third phase begins once the purely geometric simplification process is completed. At this final stage, the designer, following the objectives related to the structural verification and validation of the calculation model, decides what is the best “idealization” from the physical and mathematical point of view.
Given the breadth and importance of the third phase of Disassembling (of the structure) and the efficient way of representing it in the calculation model, to this topic will be dedicated the fourth appointment with the FEM analysis in Kyma.
The structural composition of a megayacht for FEM analysis
Kyma’s approach, to best represent the structure of a megayacht, typically metallic, is to divide it into five structural types that the FEM analyst must always evaluate and analyze for a correct defeaturing and for the subsequent steps of pre-processing:
● Plating: the plating panels’ sheet that make up the structure of a megayacht (divided into hull plating panels, decks, bulkheads, etc.), thanks to the thickness much lower than the other two dimensions (length and width) during the preparation of the CAD model are typically simplified by using surfaces.
In some special cases, moreover, the characterization of a portion of plating can be implemented in the calculation model using lines (for example with the representation of the portion of planting collaborating with a beam, called effective width of plating).
● Primary structures: this type of structures, arranged both longitudinally and transversely, are typically composed of web and faceplate. Having a length (called beam span) much greater than the other two dimensions (width and depth) and depending on the type of analysis to be developed, the primary structures are generally represented geometrically by one of the following methods:
- both the web and the plate using surfaces;
- the web using surfaces and the plate using lines;
- both the web and the plate using lines.
● Secondary structures: For secondary structures may be used the same preparation methods listed for primary structures. In the nautical field the preferred choice remains simplify the secondary structures using lines, in order to speed up the preparation of the calculation model.
The Kyma’s method of working
The correct preparation of the calculation model is thus outlined in all its articulations and its fundamental phases, customized and defined for each ship structure analyzed.
This modus operandi in Kyma has been developed, improved and enhanced over the years thanks to the hundreds of practical experiences and specific skills reserved for this sector.
The development of its own internal procedure, in fact, allows to optimize time and resources and cancel the analysis errors related to the preparatory phase to refine and program the correct workflow of this crucial and fascinating phase.